Thalassemia in Children :
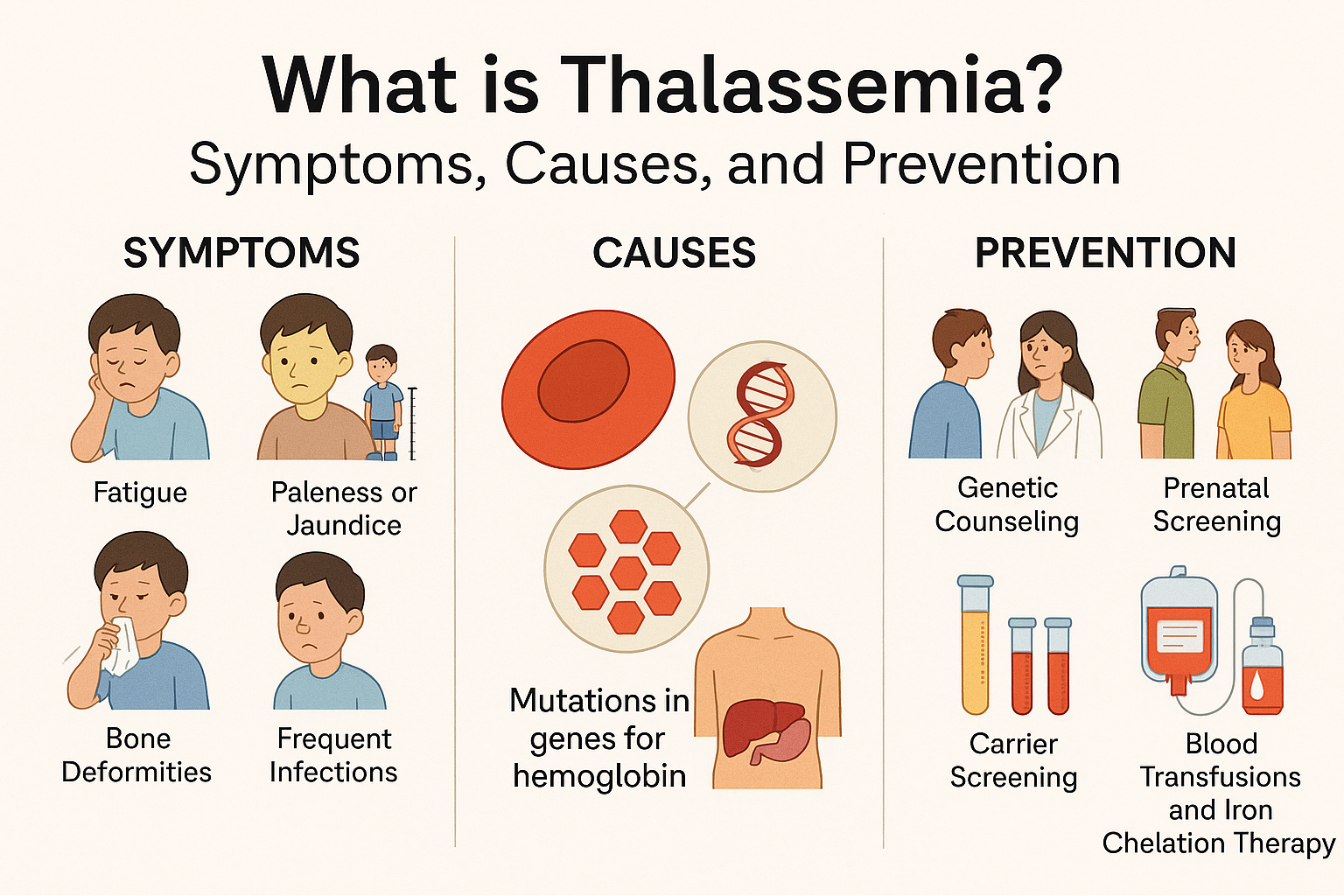
Thalassemia is an inherited blood disorder where the body produces an abnormal form of hemoglobin, leading to excessive destruction of red blood cells and anemia. In children, thalassemia can range from mild (minor) to severe (major), requiring lifelong management or potentially curative treatments like bone marrow transplantation.
Types of Thalassemia
-
Alpha Thalassemia
-
Beta Thalassemia (Major/Minor)
-
Hemoglobin H Disease
-
Thalassemia Intermedia
Common Symptoms
-
Fatigue & Pale Skin
-
Delayed Growth & Development
-
Bone Deformities (in severe cases)
-
Enlarged Spleen/Liver
Treatment Options:
-
Regular blood transfusions for thalassemia major to manage anemia effectively
-
Iron chelation therapy to prevent organ damage from iron overload
-
Curative bone marrow transplantation for eligible patients with compatible donors
-
Advanced gene therapies as emerging treatments for long-term disease management